Gallopamil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Methoxyverapamil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H40N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 484.637 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
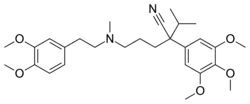
Gallopamil (INN) is an L-type calcium channel blocker that is an analog of verapamil. It is used in the treatment of abnormal heart rhythms.[1]
Synthesis
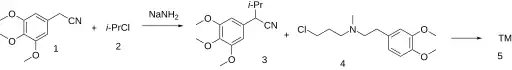
The alkylation reaction of 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetonitrile (1) and isopropyl chloride (2), using sodium amide as base gives the intermediate nitrile (3). A second alkylation with a specific alkyl chloride (4) yields gallopamil.[2][3][4]
References
- ^ Sewing KF, Hannemann H (1983). "Calcium channel antagonists verapamil and gallopamil are powerful inhibitors of acid secretion in isolated and enriched guinea pig parietal cells". Pharmacology. 27 (1): 9–14. doi:10.1159/000137824. PMID 6310646.
- ^ US patent 4115432, Dengel, Ferdinand, "Method for making basically-substituted phenylacetonitriles", issued 1978-09-19, assigned to Knoll GmbH
- ^ Theodore LJ, Nelson WL (1987). "Stereospecific synthesis of the enantiomers of verapamil and gallopamil". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 52 (7): 1309–1315. doi:10.1021/jo00383a026.
- ^ "Gallopamil". Thieme. Archived from the original on 2024-06-25. Retrieved 2024-07-02.