Piperocaine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.784 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H23NO2 |
| Molar mass | 261.365 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Piperocaine is a local anesthetic drug developed in the 1920s and used as its hydrochloride salt for infiltration and nerve blocks.
Synthesis
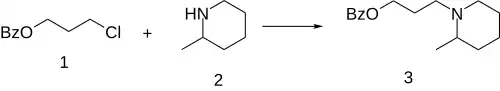
Alkylation between 3-chloropropyl benzoate [942-95-0] (1) and Pipicoline [109-05-7] (2) provides piperocaine (3).
See also
References
- ^ McElvain, S. M. (1927). "PIPERIDINE DERIVATIVES IV. SUBSTITUTED PIPERIDINE-ALKYL BENZOATES AND PARA-AMINOBENZOATES". Journal of the American Chemical Society 49 (11): 2835–2840. doi:10.1021/ja01410a030.
- ^ Samuel M Mcelvain, U.S. patent 1,784,903 (1930).
Further reading
- Tiedt TN, Albuquerque EX, Bakry NM, Eldefrawi ME, Eldefrawi AT (November 1979). "Voltage- and time-dependent actions of piperocaine on the ion channel of the acetylcholine receptor". Molecular Pharmacology. 16 (3): 909–21. PMID 316855.[1]</ref>
- ^ Costich, Emmett R. (1950-02-01). "A Preliminary Study of the Efficiency of Piperocaine Hydrochloride as a Local Anesthetic in Dental Surgery". The Journal of the American Dental Association. 40 (2): 163–169. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.1950.0022. ISSN 0002-8177. PMID 15402120.