Tolazamide
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tolinase |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682482 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | metabolized in the liver to active metabolites |
| Elimination half-life | 7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (85%) and fecal (7%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.262 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
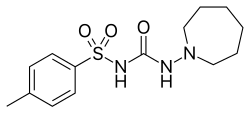
| Formula | C14H21N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 311.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tolazamide is an oral blood glucose lowering drug used for people with Type 2 diabetes. It is part of the sulfonylurea family (ATC A10BB).
Synthesis

The reaction between p-toluenesulfonamide (1) and ethyl chloroformate (2) in the presence of base gives tosylurethane [5577-13-9] (3). Heating that intermediate with azepane (4) leads to the displacement of the ethoxy group and the formation of tolazemide (5).[1][2][3][4][5]
Azepane proper would lead to [13078-23-4].
References
- ^ Vardanyan, Ṛuben, Hruby, V. J. (2006). Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier. ISBN 9780444521668.
- ^ Wright JB, Willette RE (July 1962). "Antidiabetic Agents. N4-Arylsulfonylsemicarbazides". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 91 (4): 815–22. doi:10.1021/jm01239a016. PMID 14056414.
- ^ John B Wright, U.S. patent 3,063,903 (1962 to Upjohn Co).
- ^ Wright John Brenton, GB 887886 (1962 to Upjohn).
- ^ DE1196200 idem Korger Gerhard, Weber Helmut, Aumuller Walter, U.S. patent 3,248,384 (1966 to Hoechst Ag).
External links
- "Tolazamide". Medline Plus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.