Naminidil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | BMS-234303; BMS234303 |
| Routes of administration | Topical[1] |
| Drug class | ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener; Vasodilator |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
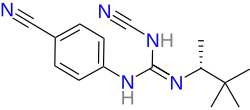
| Formula | C15H19N5 |
| Molar mass | 269.352 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Naminidil (INN, USAN; developmental code name BMS-234303) is an ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener with vasodilator activity which was under development as a topical medication for the treatment of androgenic alopecia (pattern hair loss) but was never marketed.[2][3][1] The drug was under development by Bristol-Myers Squibb and reached phase 2 clinical trials by 2001.[2] One of the phase 2 trials compared naminidil, minoxidil, and placebo for alopecia.[1] However, no results of the study appear to have been made available.[1] Development of naminidil was discontinued by 2008.[2] In terms of chemical structure, naminidil is a guanidine derivative and is structurally distinct from minoxidil.[2][4]
See also
- List of investigational hair loss drugs
- ATP-sensitive potassium channel § Stimulation of hair growth
References
- ^ a b c d Poulos GA, Mirmirani P (February 2005). "Investigational medications in the treatment of alopecia". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 14 (2): 177–184. doi:10.1517/13543784.14.2.177. PMID 15757393.
- ^ a b c d "Naminidil". AdisInsight. 17 January 2008. Retrieved 23 July 2025.
- ^ "Delving into the Latest Updates on Naminidil with Synapse". Synapse. 20 July 2025. Retrieved 23 July 2025.
- ^ "Naminidil". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 24 July 2025.