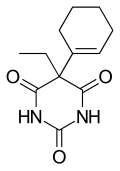
Cyclobarbital
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.127 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 236.271 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Cyclobarbital, cyclobarbitol or cyclobarbitone refers to a barbiturate derivative developed in the early 1970s in the Soviet Union.[2]
It was available in Russia until 2019, marketed and distributed as Reladorm, a fixed-dose combination pairing 100 mg cyclobarbital and 10 mg diazepam (a benzodiazepine anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant) indicated for treating insomnia before it was discontinued in 2019.
References
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Breimer DD, Winten MA (March 1976). "Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of cyclobarbital calcium in man after oral administration". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 09 (5–6): 443–50. doi:10.1007/bf00606563. PMID 989475. S2CID 20271169.