Enallylpropymal
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Enallylpropymal |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.876 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
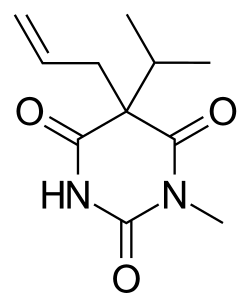
| Formula | C11H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 224.260 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Enallylpropymal (Narconumal) is a barbiturate derivative developed by Hoffman la Roche in the 1930s.[1] It has sedative and hypnotic effects and is considered to have a moderate abuse potential.[2]
References
- ^ US 2072829, Schnider O, "N-Methyl-5,5-allylisopropylbarbituric acid", issued 2 March 1937, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche Inc.
- ^ Eddy NB, Halbach H, Isbell H, Seevers MH (1965). "Drug dependence: its significance and characteristics". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 32 (5): 721–33. PMC 2555251. PMID 5294186.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.