Nepadutant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Injection[1][2] |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | <3% (oral)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 44 minutes (IV)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
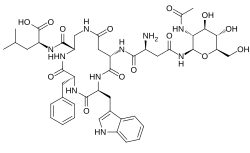
| Formula | C45H60N10O14 |
| Molar mass | 965.031 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Nepadutant (INN; development code MEN-11420) is a glycosylated bicyclic cyclohexapeptide drug which acts as a highly selective NK2 receptor antagonist.[2][3][4] It was developed by the Menarini Group and investigated for the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders and asthma but was never marketed.[3][5][6]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Academic Press. 8 September 1999. pp. 56–. ISBN 978-0-08-058378-5.
- ^ a b Holzer P (17 June 2004). Tachykinins. Springer. pp. 224–226. ISBN 978-3-540-20690-3.
- ^ a b Regitz-Zagrosek V (2 October 2012). Sex and Gender Differences in Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 489–. ISBN 978-3-642-30726-3.
- ^ Royal Society of Chemistry (Great Britain) (January 2003). Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-242-5.
- ^ Frank B (29 June 2011). Women's Issues in Gastroenterology, An Issue of Gastroenterology Clinics. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 54–55. ISBN 978-1-4557-1220-5.
- ^ Jancso G (27 November 2008). Neurogenic Inflammation in Health and Disease. Elsevier. pp. 297–. ISBN 978-0-444-53229-9.