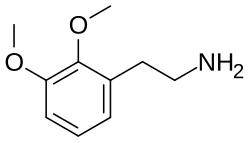
2,3-Dimethoxyphenethylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2,3-DMPEA; DMPEA-2 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.154.035 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 181.235 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
2,3-Dimethoxyphenethylamine (2,3-DMPEA), also known as DMPEA-2, is a drug of the phenethylamine family related to the psychedelic drug mescaline (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine).[1][2] It is one of the positional isomers of dimethoxyphenethylamine.[1]
In contrast to various other phenethylamines like β-phenethylamine and amphetamine, it showed little activity in terms of induction of norepinephrine release in vitro.[3] The effects of 2,3-DMPEA in humans have not been reported and are unknown.[1]
2,3-DMPEA was first described in the scientific literature by at least 1965.[1][2] It was included as an entry in Alexander Shulgin's 2011 book The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds.[1]
See also
- Substituted methoxyphenethylamine
- Dimethoxyphenethylamine
- 2,3-Dimethoxyamphetamine
- Isomescaline (2,3,4-trimethoxyphenethylamine)
References
- ^ a b c d e Shulgin A, Manning T, Daley PF (2011). "#46. 2,3-DMPEA". The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. Vol. 1. Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. pp. 81–82. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0. OCLC 709667010.
- ^ a b Clark LC, Benington F, Morin RD (May 1965). "The effects of ring-methoxyl groups on biological deamination of phenethylamines". J Med Chem. 8 (3): 353–355. doi:10.1021/jm00327a016. PMID 14323146.
- ^ Benington F, Morin RD (July 1968). "The chemorelease of norepinephrine from mouse hearts by substituted amphetamines". J Med Chem. 11 (4): 896–897. doi:10.1021/jm00310a048. PMID 5677681.
External links